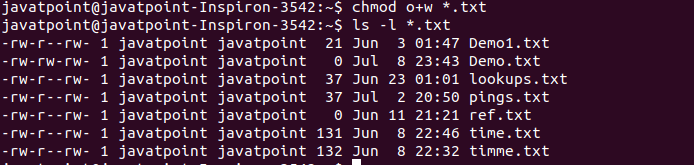
Chmod urwx,gorx filename All permission to everyone (not recommended) chmod ugorwx filename Using Octal Notation Using the octal notation you can set permissions in number between 07 Each number is calculated with the sum of read (4), write (2) and execute (1) For example, if you set permission 6, it means 42 (read write)Control who can access files, search directories, and run scripts using the Linux's chmod command This command modifies Linux file permissions, which look complicated at first glance but are actually pretty simple once you know how they workUnix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions Also Read 40 Best Examples of Find Command in Linux Example 1 How to check chmod command version If you want to check chmod command version then you need to use chmod version command as shown below As you can see from below output current chmod version is 2
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux
Chmod linux command example
Chmod linux command example-Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions With the concepts mentioned in this article, you are equipped with sufficient knowledge to handle permissions in Linuxbased distrosChmod x myfile Gives everyone execute permission on myfile chmod ugox myfile Same as the above command, but specifically specifies user, group and other



How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx
To have combination of permissions, add required numbers For example, for read and write permission, it is 42 = 6 3 chmod Examples Give read, write and execute to everybody (user, group, and others) read, write and execute = 4 2 1 = 7 $ chmod 777 filetxt (or) $ chmod ugorwx filetxt Give execute privilege to userWhat is chmod ?Repulsively remove the write permission for other users chmod R ow dirname
Explanation chmod COMMAND chmod command allows you to alter / Change access rights to files and directories File Permission is given for users,group and others as, EXAMPLE To view your files with what permission they are ls altIf you are new to Linux, and are looking for a way to change file/directory permissions through the command line, you'll be glad to know there exists a command dubbed chmod that lets you easily do this In this tutorial, we will discuss the basics of this command as well as provide examples explaining how it can be used in various scenariosLinux Commands Linux chmod Example 3 years ago by Shubham Aggarwal In this quick tutorial, we will see how we can use chmod command in an Ubuntu machine to find, modify and remove user permissions from specific files which exist on the user's file system
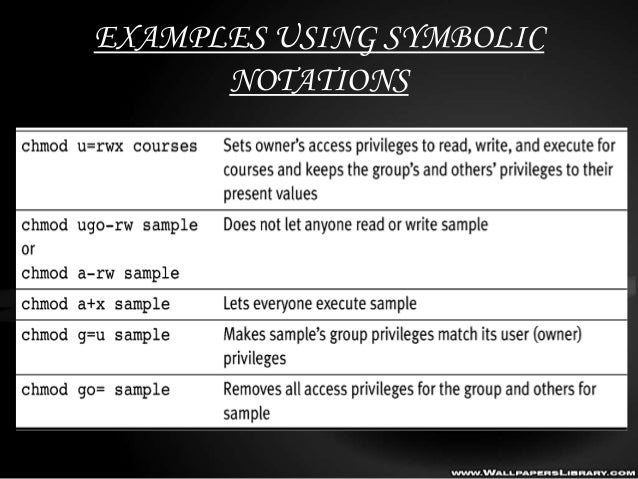
Below are some examples of how to use the chmod command in symbolic mode Give the members of the group permission to read the file, but not to write and execute it chmod g=r filename;Examples Using chmod # Below are examples of making changes to permissions chmod ux myfile Gives the user execute permission on myfile;To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules



How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux



Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples
To make a script executable use x or ux, for example $ chmod ux hello_scriptsh Step 5 Running Executable Script After you have assigned the executable permissions to the script, you can run the script without bash command as shown $ /hello_scriptshIn this example of chmod command in UNIX we will see how to remove various permissions from files You can easily remove read, write, or execute permission from a file using chmod command in both numeric and text format Below examples shows the removal of execute permission represented by –x in text formatOthers can read only" chmod R 755 myfiles Recursively (R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755 User can read, write, and execute;



How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux


Linux Chmod Command Javatpoint
We can sort it as a user, group and other from left to right, which comes in 3 blocks after the first characterFor example, to set the sticky bit, prefix a 1 to the number sequence chmod 1755 participants With a sticky bit, only the file owner, the directory owner, or the root superuser can delete the file, regardless of the file's readandwrite group permissionsA stepbystep guide with Video Tutorials, Commands, Screenshots, Questions, Discussion forums on chmod Command in Linux with Examples LinuxHelp chmod command means change modechmod is used to alter the permission of files and folders There are three basic modes to files and directories r



How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples



Solved File Permissions In Linux Can Be Set Using A 3 Dig Chegg Com
Explanation chmod COMMAND chmod command allows you to alter / Change access rights to files and directories File Permission is given for users,group and others as, EXAMPLE To view your files with what permission they are ls altControl who can access files, search directories, and run scripts using the Linux's chmod command This command modifies Linux file permissions, which look complicated at first glance but are actually pretty simple once you know how they workIn Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command Chmod stands for "Change Mode" and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux The command is relatively simple to use and involves using



Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod



Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech
To make a script executable use x or ux, for example $ chmod ux hello_scriptsh Step 5 Running Executable Script After you have assigned the executable permissions to the script, you can run the script without bash command as shown $ /hello_scriptshChmod command is used to change access permission of files and directories in Linux operating systemschmod stands for change modeAccess permissions specify whether a user account or group can read, write, or execute a given file and directory chmod Command SyntaxTo check the options that are available in chmod, we can do by using Linux command man chmod Examples of chmod Command in Linux Following are the examples of chmod commands in Linux explained in detail 1 chmod Command using Operator Method Let us take an example where a file test_filetxt has full permission to the owner, group and other



Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials



Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize
Linux chmod command is one of the most commonly used commands especially by system administrators when assigning modifying file and folder permissions It's usually used when installing and configuring various services and features in a Linux systemUsing "Chmod x" Command on Linux and Unix with Examples In Linux systems, " chmod " command is used to determine the access rights of users to files It allows us to change the access permissions of the files we specify The exact equivalent of chmod is change modeBut now we will see the usages of chmod 755 on a Linux system The main difference between the chmod R 755 and the chmod 755 is, the R 775 allows all users to modify the entire directory, where the 775 command only allows the root user to read and write the



11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub



Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples
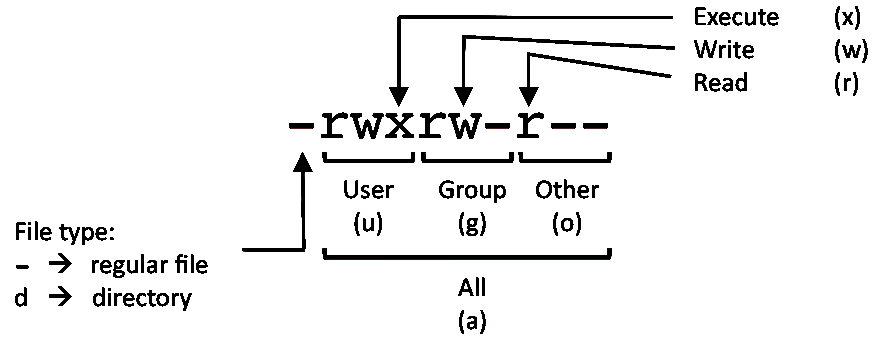
Linux chmod command examples (all users) Given that extremely brief background on Unix/Linux file permissions, here is a collection of Unix chmod commands In each example, assume we start with a file named footxt that has no assigned permissions, like this I'll then show the file permissions after the command I issueEvery file in the Linux / macOS Operating Systems (and UNIX systems in general) has 3 permissions Read, write, execute Go into a folder, and run the ls al command The weird strings you see on each file line, like drwxrxrx, define the permissions of the file or folder Let's dissect itLinux chmod Command Help and Examples computerhopecom Random CHMOD Examples CHMOD 717 CHMOD 752 CHMOD 524 CHMOD 112 CHMOD 011 CHMOD 362 CHMOD 135 CHMOD 756 CHMOD 666 CHMOD 111 CHMOD 3 CHMOD 511 CHMOD 073 CHMOD 440 CHMOD 371



Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices


Linux Command Cheat Sheet
Link nardi June 8, 10, 559 amIn Unixlike operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file The name is an abbreviation of change mode Syntax chmod referenceoperatormode file The references are used to distinguish the users to whom the permissions apply ie they are list of letters that specifies whom to give permissionsHow to use the chmod command in Linux First, open terminal Then use the cd command to go to the directory where the file you want edit is Now use the following command to see the permission granted to the file Ls –l filename Now you just need to use the attributes explained above Use the following example to execute the chmod command in
.png)


File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change



Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets
Previously, we have seen the use of the chmod R 755 command for Linux systems;Chmod ow file2 You can combine multiple references and modes to set the desired access all at once For example, to explicitly make file3 readable and executable to everyone chmod ugo=rx file3 The all (a) mode is the same as ugo, allowing the previous command to be expressed as chmod a=rx file3The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CH ange MOD e Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others
/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)


Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights



File Permissions In Unix Linux Chaitanya Rahalkar
Linux chmod command is one of the most commonly used commands especially by system administrators when assigning modifying file and folder permissions It's usually used when installing and configuring various services and features in a Linux systemThe Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode chmod has two operating modes symbolic mode;Several symbolic methods are equivalent;



Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux
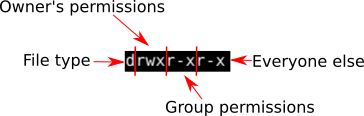


Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples
How to use the chmod command in Linux First, open terminal Then use the cd command to go to the directory where the file you want edit is Now use the following command to see the permission granted to the file Ls –l filename Now you just need to use the attributes explained above Use the following example to execute the chmod command inThis tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examplesBelow are some examples of how to run and use the chmod on Ubuntu Linux If you're a owner of a file called Confidential and want to change the permisions or modes so that user can read / write and execute, group members can read and execute only and others can only read, you will run the commands below sudo chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=r Confidential



Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks



File Permissions In Linux Using Chmod Command
To check the options that are available in chmod, we can do by using Linux command man chmod Examples of chmod Command in Linux Following are the examples of chmod commands in Linux explained in detail 1 chmod Command using Operator Method Let us take an example where a file test_filetxt has full permission to the owner, group and otherChmod command is used to change access permission of files and directories in Linux operating systemschmod stands for change modeAccess permissions specify whether a user account or group can read, write, or execute a given file and directory chmod Command SyntaxThe chmod() function shall change S_ISUID, S_ISGID, S_ISVTX, and the file permission bits of the file named by the pathname pointed to by the path argument to the corresponding bits in the mode argument The application shall ensure that the effective user ID of the process matches the owner of the file or the process has appropriate privileges in order to do this



What Did We Do When We Were Chmod 777 Develop Paper



7 Examples Of Command Chmod On Linux And Explanation
Chmod Linux Commands What is Linux chmod Command?Here is an example # chmod t allAccess/ # ls ld allAccess/ drwxrwxrwx 2 himanshu himanshu 4096 Oct 24 1619 allAccess/ Different OS behave differently with sticky bits as explained in this wikipedia article For example, Linux only looks for sticky bit if a user tries to rename a file It will not check the sticky bit if a file is beingSudo chmod R 755 Example The command gives read, write, and execute privileges to the owner ( 7 ) and read and execute access to everyone else ( 55 ) Note In the example above, the permission is defined using the octal/numerical mode ( 755 )


Working With File Permissions On Your Raspberry Pi Dummies


Linux Chmod Tips
Chmod Linux Commands What is Linux chmod Command?Group members and other users can read and execute, but cannot writeRemove the execute permission for all users chmod ax filename;



Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks



Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
In Linux systems, "chmod" command is used to determine the access rights of users to filesIt allows us to change the access permissions of the files we specify The exact equivalent of chmod is change mode When we examine the example below;Chmod ( Change Mode ) is a command line utility in Unix , Linux and other Unix like systems to change the read, write, execute permissions of a file for owner , group and others How to use chmod?For example $ chmod 755 R directory_name $ chmod 755 R /home/linuxtechi/data Example 3) Assign permissions using text notation Another way of assigning permissions is by using the text notation In this method, the chmod command takes flags or symbols which represent the owner, group, others or all users ( u, g , and o) in the syntax



Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners



How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
The chmod() function shall change S_ISUID, S_ISGID, S_ISVTX, and the file permission bits of the file named by the pathname pointed to by the path argument to the corresponding bits in the mode argument The application shall ensure that the effective user ID of the process matches the owner of the file or the process has appropriate privileges in order to do thisA stepbystep guide with Video Tutorials, Commands, Screenshots, Questions, Discussion forums on chmod Command in Linux with Examples LinuxHelp chmod command means change modechmod is used to alter the permission of files and folders There are three basic modes to files and directories rLearn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examples Permission levels and types Each file and directory has three permission levels (user, group and other) and three types of permission (read, write and execute) in each level



Linux And Unix Chmod Command Tutorial And Examples Xsofthost



Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Ged as Chmod Command, Chmod Examples, Linux Chmod Examples, Unix Chmod Examples {26 comments add one} Egor June 8, 10, 332 am I think correct command for the p3 in accordance with its subject should be $ chmod urw filename, don't I?This tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examplesIn this article, I'll share with you some of the practical examples of chmod command I'll also explain some the popular terms like chmod 777 or chmod 755 or chmod r Before you see the chmod examples, I would strongly advise you to learn the basics of file permissions in Linux



8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut
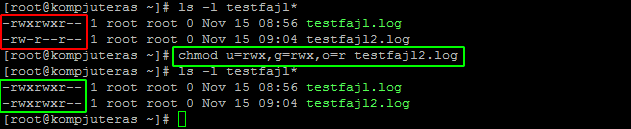


How To Display File Permissions In Octal Format In Linux Kompjuteras
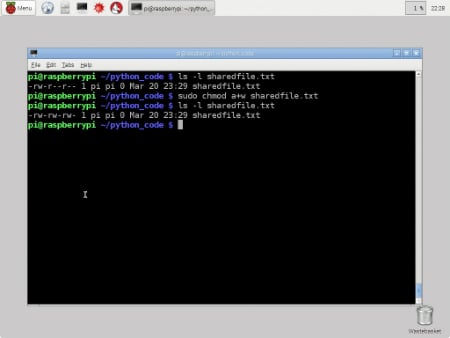
The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CHange MODe Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others This type of restriction is useful for effective file/folder management, securing system and providing a levelIn this file example, sets read and write permissions for user and group $ chmod ug=rw /var/www/html/dataphp See "how to use change user rights using chomod command" for more information Conclusion We explained the chown and chmod command for Linux and Unix usersIn general, the system for Unix data rights relies on user classes and individual access rights Chmod supports two different systems the symbolic notation using letters and allocation of data rights through digitbased octal codesAs previously mentioned, changes to access rights can only be made by the file owner or root user



How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples



Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions
One example is chmod u=rwx,go=rx,ot Extras The letter a is a shortcut to assign permissions to all users The command chmod arwx is equivalent to chmod ugorwx Recursive Like many other Linux commands, chmod has a recursive argument, R, which allows you to operate on a directory and its contentsTo change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rulesLinux Commands Linux chmod Example 3 years ago by Shubham Aggarwal In this quick tutorial, we will see how we can use chmod command in an Ubuntu machine to find, modify and remove user permissions from specific files which exist on the user's file system



Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier



Using Chmod X Command On Linux And Unix With Examples Systemconf
Group can read only;Examples chmod 644 filehtm Set the permissions of filehtm to "owner can read and write;Here is an example # chmod t allAccess/ # ls ld allAccess/ drwxrwxrwx 2 himanshu himanshu 4096 Oct 24 1619 allAccess/ Different OS behave differently with sticky bits as explained in this wikipedia article For example, Linux only looks for sticky bit if a user tries to rename a file It will not check the sticky bit if a file is being



Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
The Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode chmod has two operating modes symbolic mode;Explanation chmod COMMAND chmod command allows you to alter / Change access rights to files and directories File Permission is given for users,group and others as, EXAMPLE To view your files with what permission they are ls altIn Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command Chmod stands for "Change Mode" and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux The command is relatively simple to use and involves using



Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu



How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux
Chmod ow file2 You can combine multiple references and modes to set the desired access all at once For example, to explicitly make file3 readable and executable to everyone chmod ugo=rx file3 The all (a) mode is the same as ugo, allowing the previous command to be expressed as chmod a=rx file3Chmod command is used in two ways 1 Using octal value & position Sets the permission for owner, group and others with octal values , 4 for read , 2 for write , 1 for execute andChmod Linux Commands What is Linux chmod Command?



How To Run Sh File In Linux How To Use Linux
.png)


File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change
Chmod urwx,gorx filename All permission to everyone (not recommended) chmod ugorwx filename Using Octal Notation Using the octal notation you can set permissions in number between 07 Each number is calculated with the sum of read (4), write (2) and execute (1) For example, if you set permission 6, it means 42 (read write)


How To Chmod Files Only On Linux
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)


How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux



9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux



Introduction To The Linux Chmod Command Opensource Com


Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This



Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples


How To Chmod Files Only On Linux



Linux Commands Chmod



How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples



How To Change Linux S Permissions Through A Practical Example Of The Chmod Command



How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux



Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples



Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks



Chmod Wikipedia



Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage



How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx



Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu
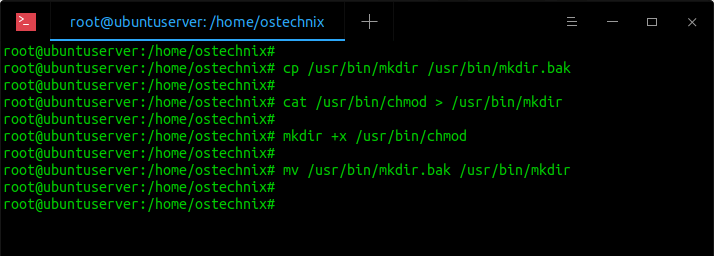


Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix
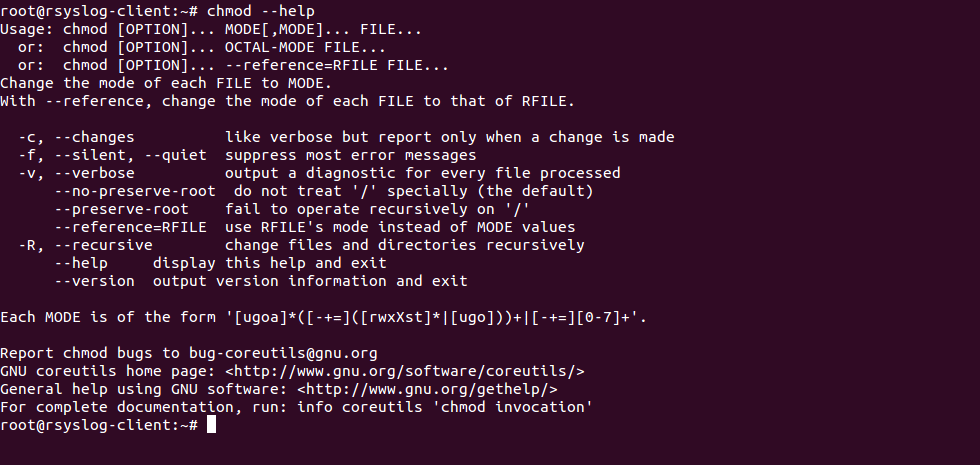


Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders



Chmod Cheatsheet Linux



Numeric Permissions Table Linux Chmod Command Linux Permissions



Linux Chmod Command Summary With Examples Youtube


Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples



9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux Linuxhowto Net



How To Use The Chmod Command On Ubuntu 16 04 18 04 With Examples Website For Students



Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube



How To Create Write A Simple Sample Linux Shell Bash Script 5 Steps Instructables



Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin



Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize



A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler



Chmod Command In Linux Operators Used In Chmod Command In Linux


How To Chmod Files Only On Linux
.png)


File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change



Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier



How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux



Chmod Help Examples How To Use Chmod In Linux Ionos



Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Computer Security


Chmod Shortcuts For Linux



How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux



Linux Chmod Example Bitcoin Exchange Script White Label Exchange 5 Min Ico Script Enterprise Blockchain Company
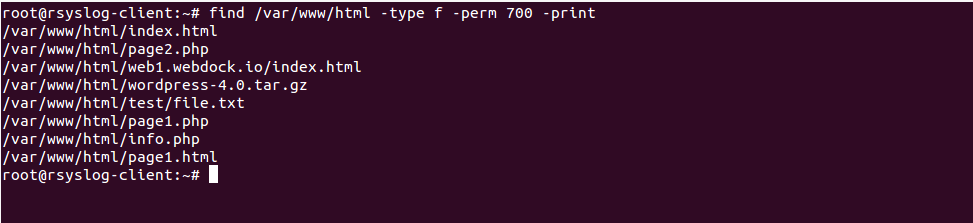


Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders



Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks



Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials


Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com



Linux Chmod Command Examples Journaldev



Linux File Permission Javatpoint



How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples



8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut



Linux Unix Changing Permissions With Chmod Vinish Kapoor S Blog



Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint



Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected



Linux For Programmers File Permissions And Chmod



Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices


Filepermissions In Linux



Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode



Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿