I think I lost (or forgot the file location) a file named tomsfirstbirthdaymp4 on my Unix based system Is there is a Unix bash shell command to find a file called "tomsfirstbirthdaymp4" in a directory and subdirectories?Chmod wx filename to take out write and executable permissions;Executing a directory doesn't really make sense, so think of this as a traverse permission A user must have execute access to the bin directory in order to execute the ls or the cd command Changing Permissions To change the file or the directory permissions, you use the chmod (change mode) command There are two ways to use chmod — the
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights
Chmod command in unix for directory and subdirectories
Chmod command in unix for directory and subdirectories-But there are many options that can be used with ls command to get the desired output Let us see some of those command examples ls ~ It will list the contents of your home directory ls / It will list the contents of the root directory ls / It will list the contents of the parent directory ls */ It will list the contents of allThe basic syntax includes using the find command to locate files/directories and then passing it on to chmod to set the permission sudo find directory type d/f exec chmod privilege {} \;
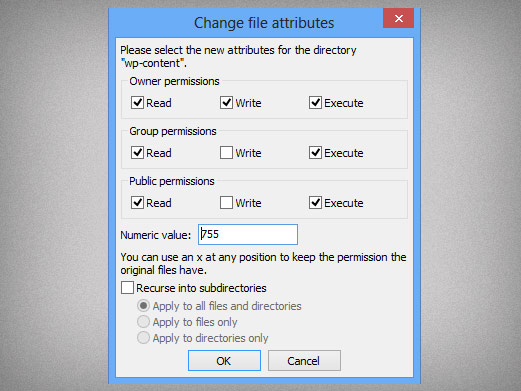


What Is Chmod How To Use Chmod For Wordpress File Permissions
Chmod command examples Using chmod command is very easy if you know what permissions you have to set on a file For example, if you want the owner to have all the permissions and no permissions for the group and public, you need to set the permission 700 in absolute mode chmod 700 filenameYou would set the sticky bit primarily on directories in UNIX / Linux If you set the sticky bit to a directory, other users cannot delete or rename the files (or subdirectories) within that directory When the sticky bit is set on a directory, only the owner and the root user can delete / rename the files or directories within that directory 1To change file access permissions you need to use the chmod command It has R or –recursive option that change files and directories recursively donotprint /donotprintThe find command can be used to find files and directories The chown command can be used to change user and group permission
Use the chmod command to change the permissions for all files, directories and it's subdirectories sudo chmod R 755 /var/www/html Note – The permission 755 is good to set for directories but not on filesClick below button to copy the code By Linux tutorial teamChmod x filename to allow executable permissions;
To make this possible you can use the find command and search for all files with a sh extension and then run the chmod command on each one found find /directory/of/interest/ type f iname "*sh" exec chmod x {} \;Example 13 "chmod gorwx * or chmod 700 *" Commands chmod gorwx * or chmod 700 * Used when inside a directory Read, write and run access permissions for the group and other users are removed from all files and subdirectories in the directory where it is usedUnix & Linux Stack Exchange is a question and answer site for users of Linux, FreeBSD and other Un*xlike operating systems and "sed" # in a single command to show the nesting of # subdirectories The setup command for PATH # works with the Bash shell (the Mac OS X default) List contents of a directory and all sub directories


9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)


Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights
Use the chmod command to change the permissions for all files, directories and it's subdirectories sudo chmod R 755 /var/www/html Note – The permission 755 is good to set for directories but not on filesThe man page for chmod doesn't list a way to recursively change permissions on directories only, without affecting the files themselves Let's say that I wanted to change the permissions on the current directory and all subdirectoriesYou would simply substitute the directory name for the file name You can also use the letters r, w, and x to set read, write, and execute permissions and the letters u, g, o, and a to specify user, group, other or all % chmod v ax myfiletxt
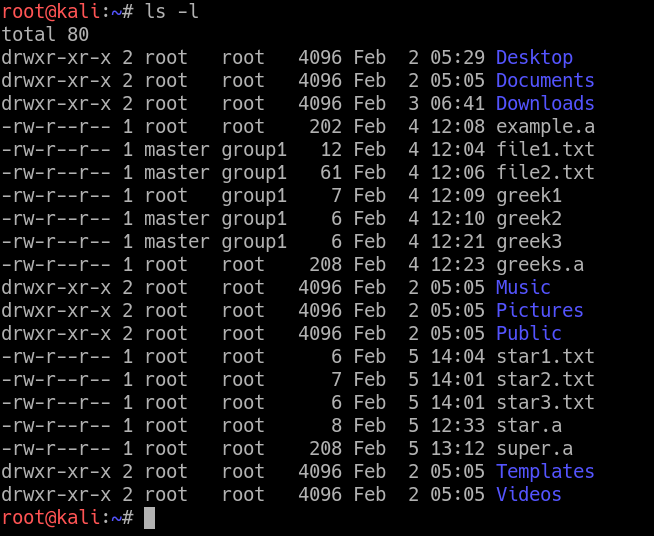


Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks



How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft
The command chmod (short for change mode) is used to change permissions for a file chmod is used a bit differently from most other Unix commands To give write permission to the group users for file1 (the first file we examined), we give the command chmod gw file1 This may be understood as followsTo set group read/execute on, group write off on /u/ateam/pgm chmod g=rx /u/ateam/pgmChmod command examples Using chmod command is very easy if you know what permissions you have to set on a file For example, if you want the owner to have all the permissions and no permissions for the group and public, you need to set the permission 700 in absolute mode chmod 700 filename



A Complete Guide To Chmod Recursive Force And More



8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut
A Few Additional chmod Tips We'll wrap up with a bit of extra advice related to chmod Remember that you need read permissions in order to list directories and subdirectories You can set all files in a folder or directory to writeable with chmod R 775 directoryInformationtype f Normal files only (skip directories, symlinks, named pipes and sockets, and the special files found in /dev)Use the chmod command to change the permissions for all files, directories and it's subdirectories sudo chmod R 755 /var/www/html Note – The permission 755 is good to set for directories but not on files
/create-directories-linux-mkdir-command-3991847-55ea75a52f7842a2af0fdfe0b7470270.gif)


How To Create Directories In Linux With The Mkdir Command


How To Chmod Files Only On Linux
Chmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions Following is a sample of ls l command output In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of usersTo set group read/execute on, group write off on /u/ateam/pgm chmod g=rx /u/ateam/pgmTo remove a directory that you own, use the rmdir command For example, to remove a subdirectory named mydir that exists in your current working directory, at the Unix prompt, enter rmdir mydir If mydir exists, and is an empty directory, it will be removed If the directory is not empty or you do not have permission to delete it, you will see



How To Make A File Folder Writable Chmod 777 Feedplatform Help Center



How To Resolve The Permission Denied Error In Linux
This command will search in the current directory and all sub directories for all files named whatYouAreLookingFor If found, the files will be processed by the chmod or command The argument'{}' inserts each found file into the chmod command line The \;Chmod is a very helpful command to change the file permissions of a file or a folder in any UNIXlike operating system Let's say you are currently in the root directory of your Unixlike system and you want to change the file permissions of a folder and all of the other files and subdirectories present inside that folder All you need to do is to run the chmod command with Recursive option RSudo find directory type d/f exec chmod privilege {} \;



Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier



Unix File Permissions Computer Science
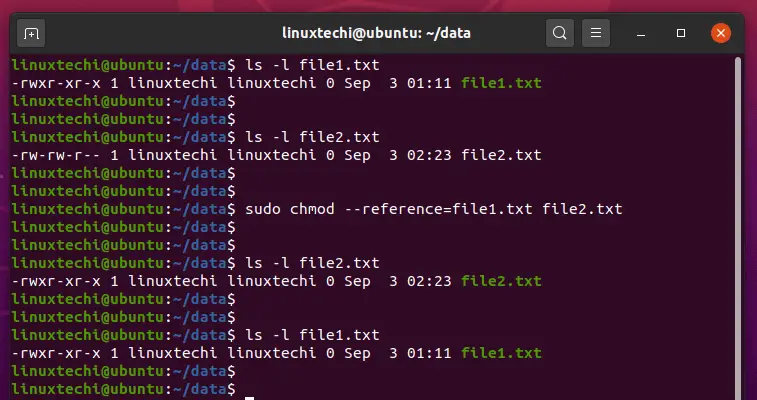
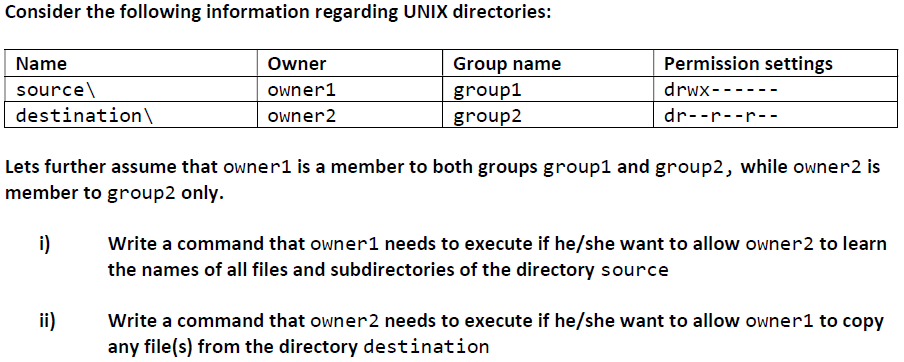
What is the command to set the execute permissions to all the files and subdirectories within the directory /home/user1/direct a) chmod r x /home/user1/direct b) chmod R x /home/user1/direct unix domain socket file c) symbolic linkWe have the root folder for our website at /etc/apache2/htdocs We chmodded that folder and all subdirectories with all the commands that you posted on here and seemed to work I go in there, create a new folder in the root and when i try to access /purch on the site it says FORBIDDEN PERMISSION ERROR I then have to chmod THAT folder to view itChmod allows you to change the permission of multiple files and subdirectories within a directory using the –R option as follows $ chmod –R reference operator mode file Let's say the subdirectories under the downloads directory have the following permissions as shown in the following screenshot
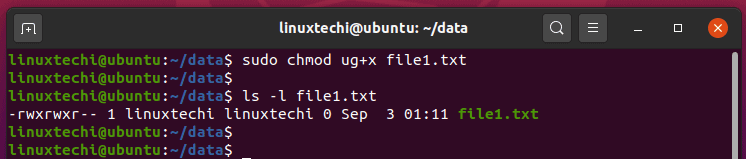


9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux



Unix Command To Find A File In A Directory And Subdirectory Nixcraft
If you want to create a directory containing several subdirectories, or a directory tree, using the command line in Linux, generally you have to use the mkdir command several times However, there is a faster way to do this Let's say we've created a directory called htg, and want to create four subdirectories within itTo set other write permission off on 2 files chmod ow file1 file2;Chmod go=r myfile The chmod command also operates on directories For example, to remove write permission for other users on a subdirectory named mydir, you would enter chmod ow mydir To do the same for the current directory, you would enter chmod ow



Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices


Making Files Transferred To Unix Accessible
To set group read/write/execute permissions on the directory /public/teamdir and all its files and subdirectories chmod R grwx /public/teamdir;The chmod command has a nice shortcut for setting the executable bit only on directories, like so chmod aX * This is very handy to make a whole directory tree readable by anyone, but not setting the executable bit on any regular files chmod R arX * Example1 chmod ar filename above command adds the read permission to all the users Exmple2 chmod ow filename above command removes the write permission from other users 12 du du (disk usage) will count the amount of disk space for a given directory, and all its subdirectories take up on the disk Example du –h dirname



Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog



Chmod Why It Matters User Permissions In Os X Droppedframe Com
The chmod command specifies which class or classes (u ser, g roup, o ther) have access to the file or directory in various modes (r ead, w rite, e xecute) Use the operators and to add or remove selected permissions for a class without changing its other permissions Use = to specify all of the permissions for a class at onceChmod Unix, Linux Command chmod To change access permissions, change mode (or access for directories) (x), execute only if the file is a directory or already has execute permission for some user (X), set user or group ID on execution (s), sticky (t), the permissions granted to the user who owns the file (u), the permissions grantedReplace directory with the directory path that holds the files and subdirectories you want to configure



Useful Unix Commands Pdf Free Download



Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu
Setting permissions for a directory follows exactly the same procedure;Chmod Command Examples In this example, you are setting permission to 0755 $ chmod R 0755 directoryNameHere However, if you need to apply conditional file permissions recursively, you need to use combination of the find and chmod command To find all files in /home/user/demo directory, enter $ find /home/user/demo type f printYou would set the sticky bit primarily on directories in UNIX / Linux If you set the sticky bit to a directory, other users cannot delete or rename the files (or subdirectories) within that directory When the sticky bit is set on a directory, only the owner and the root user can delete / rename the files or directories within that directory 1



How To Change Permissions In Linux



Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather
Argument indicates the exec command line has endedChmod has the recursive option that allows you to change the permissions on all the files in a directory and its subdirectories chmod R 755 directory chmod 777 Everything for everyone You might have heard of chmod 777 This command will give read, write and execute permission to the owner, group and public If you want to change the mode to 777, you can use the command like this chmod 777 filenameChmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions Following is a sample of ls l command output In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users



Chmod Changing Permissions Of Operation Not Permitted Unix Linux Stack Exchange



The Unix File System
Related Commands What is chmod?If we change the mode again using the command % chmod v 765 myfiletxt mode of `files/myfiletxt' changed to 0644 (rwrr) then the ls l myfiletxt command would show as the permissionsrwxrwrx Naturally, only the owner can modify the permissions for a file or directory Directory vs File Permissions UNIX is a "topdownRelated Commands What is chmod?



How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux



Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
To set other write permission off on 2 files chmod ow file1 file2;This is how you can change the directory permissions in Linux recursively To apply the same recursive permissions to all the file and subdirectory, use –R option while to apply recursive permissions to file and subdirectories separately, use the Find commandChmod (change mode) is one of the most frequently used commands in unix or linux operating system The chmod command is used to change the file or directory access permissions To know about the access permissions of a file or directory, use the ls l command as shown below $ ls l samplesh rwxrwr 1 matt deploy 94 Oct 4 0312 samplesh



Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod


Solved Edit I Apologize I Ve Been A Fool And Mistakenly Chegg Com
A Few Additional chmod Tips We'll wrap up with a bit of extra advice related to chmod Remember that you need read permissions in order to list directories and subdirectories You can set all files in a folder or directory to writeable with chmod R 775 directoryChmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions Following is a sample of ls l command output In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users*Updated 8/14/19* How to change directory permissions in Linux To change directory permissions in Linux, use the following chmod rwx filename to add permissions;


Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line



Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Replace directory with the directory path that holds the files and subdirectories you want to configure Specify whether it is searching for a directory type d or a file type f Set the file privilege with the chmod command using the numerical or symbolic modeTo set group read/write/execute permissions on the directory /public/teamdir and all its files and subdirectories chmod R grwx /public/teamdir;For a directory, the permissions govern who can cd into the directory and who can create, or modify files within the directory You use the chmod command to set each of these permissions To see what permissions have been set on a file or directory, we can use ls Viewing and Understanding File Permissions



Write A Unix Linux Find Like Command Myfind In Chegg Com



Unix Commands Reference
Chmod has the recursive option that allows you to change the permissions on all the files in a directory and its subdirectories chmod R 755 directory chmod 777 Everything for everyone You might have heard of chmod 777 This command will give read, write and execute permission to the owner, group and public If you want to change the modeUsing Options with chmod and chown Commands Option is an additional command to change the output of a command One of the most popular options that you can combine with chmod and chown is R (Recursive) This Linux option allows you to change permissions or owners of all files and subdirectories inside a specific directoryThe chmod command is used to change the permission settings on a file or directory



Chmod Why It Matters User Permissions In Os X Droppedframe Com



Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu
Chmod rwx directoryname to remove permissions;To make the chown command recursively operate on files and directories, use the R commandline option chown R newownernewgroup directorynameorpath For those who aren't aware, recursive means the operation will be performed for all files in the given directory, as well as for files and directories within all subdirectories Q7Linux Solution 1 chmod R 755 will set this as permissions to all files and folders in the tree You can use the find command For example To change all the directories to 755 (drwxrxrx) find /opt/lampp/htdocs type d exec chmod 755 {} \;



Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod


Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples
You need to use the find command on a Linux or Unixlike system to search through directories for filesWhat is the command to set the execute permissions to all the files and subdirectories within the directory /home/user1/direct a) chmod r x /home/user1/direct b) chmod R x /home/user1/direct c) chmod f r x /home/user1/direct d) chmod F x /home/user1/direct Submitted by MurtazaNote that "r" is for read, "w" is for write, and "x



Delete Remove A Directory Linux Command Nixcraft



Chmod Wikipedia
The chmod command is used in Linux (and Unixlike systems) to set the permissions of files and directories First of all, here is the generic syntax of the chmod command chmod The permission part of the command can have different formats One format is a group of number like the one you see below



An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
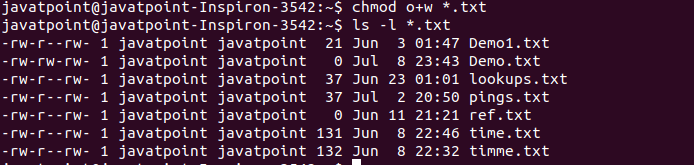


Linux Chmod Command Javatpoint
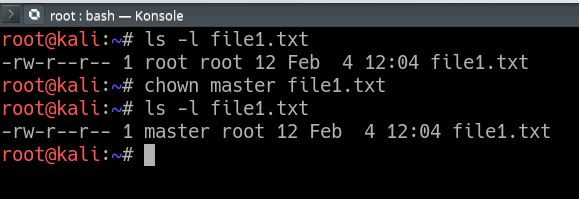


Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)


How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux



How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux



Linux Commands Chmod Cloudaffaire



How To Create A Directory In Linux With Mkdir Command Examples



Setting File And Directory Permissions Computational And Information Systems Laboratory



Unix Linux Os X File Permissions
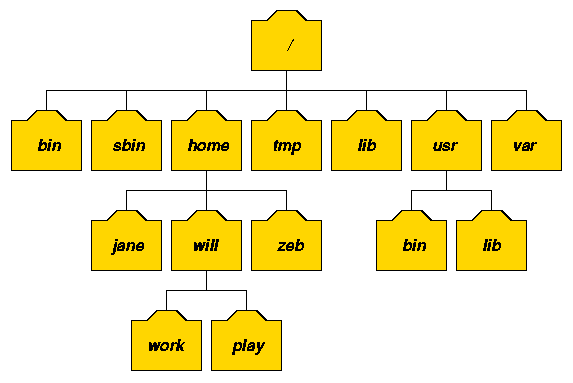


Javarevisited How To Create Complex Directory Tree Using Mkdir P Command In Unix



Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode



Delete Remove A Directory Linux Command Nixcraft



Top 15 Frequently Asked Linux And Unix Interview Questions And Answers For Beginners And Experienced Java67
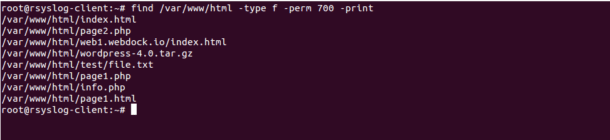


Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders



Chapter 2 Exploring The Unix File System For Tuesday Section File And File Systems Ppt Download



Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux



File Security


Unix Commands Basic To Advanced Unix Commands With Example



Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange



Linux Tutorial



How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight



Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples
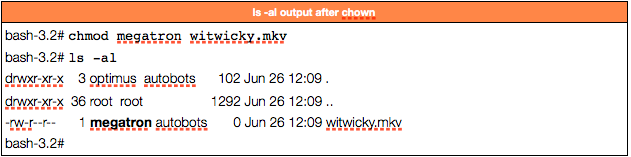


Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support


An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World



Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples



Top 10 Courses To Learn Linux Command Line In Best And Free In Linux Online Learning Analyzing Text



Linux Chmod Recursive How To Change File Permissions Recursively



How To Change Bulk File Permissions Recursively 2daygeek



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission



Chmod 777 Tutorial The Electric Toolbox Blog



Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support



Ls Wikipedia



What Is Chmod How To Use Chmod For Wordpress File Permissions



Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu



Linux Tutorial


Unix Tutorial Five
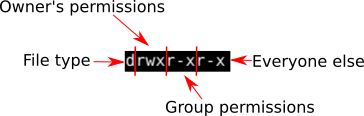


Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples



Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command



How To Make A File Folder Writable Chmod 777 Feedplatform Help Center



Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather



9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux


Hdfs File System Commands Hadoop Online Tutorials



Unix Permissions


Permissions And Executables A Primer For Computational Biology


Working With Files And Directories



How Can I Recursively Change The Permissions Of Files And Directories Ask Ubuntu



What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize



Zyps93yz6ze 9m



How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux



File And Directory Permissions In Linux Freebsd Masos Tech



Basic Linux Usage



Solved 1 Which Of The Following Commands Or Sequences Of Chegg Com



How To Recursively Change The File S Permissions In Linux Linuxize



Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks



Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org
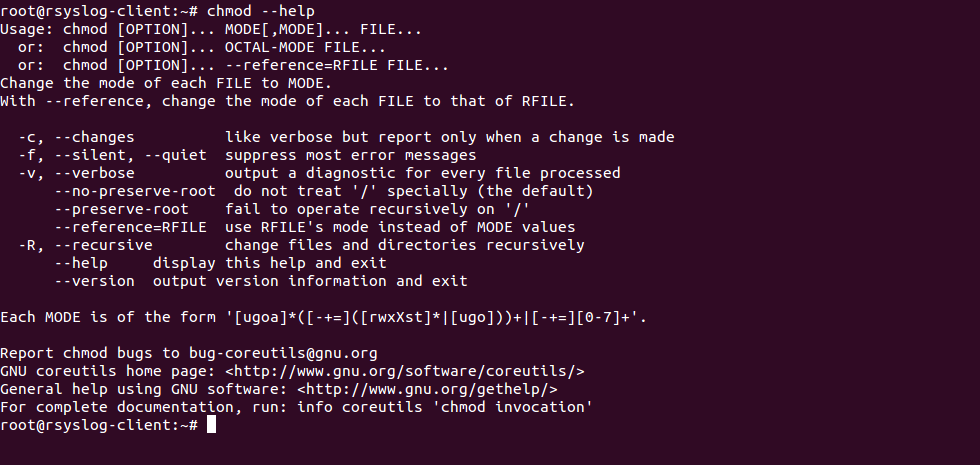


Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders
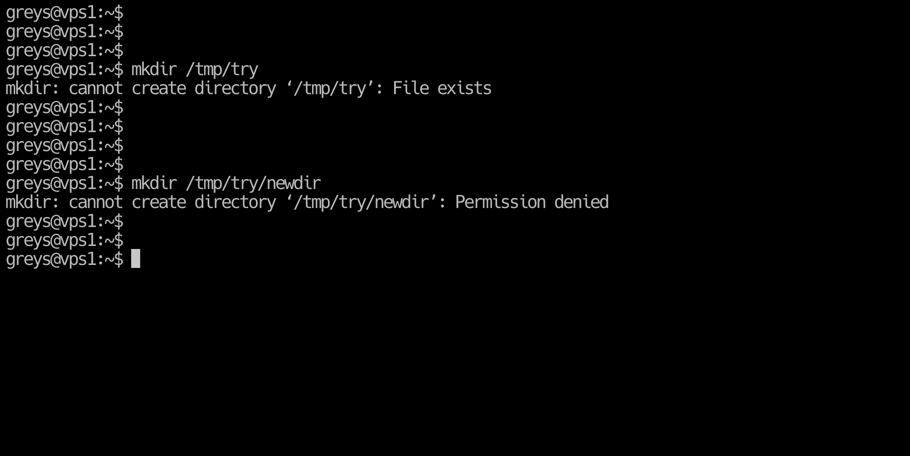


Mkdir Cannot Create Directory



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿